



Next: Contents
Up: PHENIX Muon Notes
 Send mail to Joel Moss
Send mail to Joel Moss
 Get postscript file
Get postscript file
Spin Structure Function Physics with an Upgraded PHENIX Muon Spectrometer
The PHENIX/Spin Collaboration
October 27, 1994
Abstract:
A major investment by the RIKEN Spin Group makes feasible a significant
enhancement of the polarized collider program of the PHENIX Detector using the
muon detection capability. The addition of a second muon end cap and
muon identification in the central rapidity region yields a detector with large
acceptance for high mass muon pairs. The upgrade makes feasible a program of polarized
quark and antiquark structure function physics using Drell-Yan continuum and vector boson
production. It also adds significantly to the array of measurements feasible for
investigating gluon polarization via heavy quark production.
The proposal of the RHIC Spin Collaboration was approved one year ago based on the
PHENIX detector of the Conceptual Design Report (CDR). The principal operational difference
in the present proposal is a request for polarized proton operating time at  .
This energy optimizes the rate of high-
.
This energy optimizes the rate of high-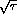 Drell-Yan pairs where large polarization
effects are most likely to be observed. It also minimizes backgrounds from competing
processes, principally semi-leptonic charm decay.
Drell-Yan pairs where large polarization
effects are most likely to be observed. It also minimizes backgrounds from competing
processes, principally semi-leptonic charm decay.
Collaborating Institutions
- PHENIX Collaborating Institutions
- Bombay Research Institute, Bombay, India
- Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973
- University of California, Riverside, Riverside, CA 92521
- Chinese Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing, China
- Chung-ang University, Seoul, Korea
- Columbia University, Nevis Labs., Irvington, NY 10533
- Institute for High Energy Physics, Academia Sinica, Beijing, China
- Institute of High Energy Physics, Protvino, Russia
- Institute of Modern Physics, Academia Sinica, Lanzhou, China
- Institute for Nuclear Research, Moscow, Russia
- Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50011
- Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia
- Korea University, Seoul, Korea
- Kurchatov Institute of Atomic Energy, Moscow, Russia
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550
- Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM 87545
- Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA 70803
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37831
- Peking University, Institute for Heavy-Ion Physics, Beijing, China
- Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia
- University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil
- Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- Soong-Sil University, Seoul, Korea
- University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
- Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN 37235
- Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
- New Institutions and Participants
- Institute for Chemical and Physical Research (RIKEN), Hirosawa,
Wako, Japan
T. Ichihara, M. Ishihara, Y. Wantanabe
Y. Wantanabe
- Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, and RIKEN
H. Enyo, K. Imai, H. Kaneko,
A. Masaike, T. Murakami, M. Yosai
- Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo,
Japan, and RIKEN
T.-A. Shibata
- New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM
G. Kyle
Spokesmen: K. Imai, Kyoto University and RIKEN
J.M. Moss, Los Alamos National Laboratory
Local Coordinators: Y. Makdisi and M.J. Tannenbaum




Next: Contents
Up: PHENIX Muon Notes
Converted to HTML from LaTeX by W. Wayne Kinnison
Sun Nov 5 18:47:30 MST 1995
 .
This energy optimizes the rate of high-
.
This energy optimizes the rate of high-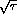 Drell-Yan pairs where large polarization
effects are most likely to be observed. It also minimizes backgrounds from competing
processes, principally semi-leptonic charm decay.
Drell-Yan pairs where large polarization
effects are most likely to be observed. It also minimizes backgrounds from competing
processes, principally semi-leptonic charm decay.