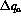 ,
specifically
,
specifically
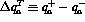 but with
but with
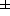 denoting the spin projection perpendicular to the momentum of the nucleon. It is
measured in the DY process with transversely polarized beams. Specifically,
denoting the spin projection perpendicular to the momentum of the nucleon. It is
measured in the DY process with transversely polarized beams. Specifically,
The transversity structure function has recently received a great deal of attention[14,15] as a
potential source of qualitatively new insight into the spin structure of the nucleon; it is not
measurable in DIS experiments. The transversity is defined in a fashion similar to 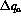 ,
specifically
,
specifically
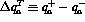 but with
but with
 denoting the spin projection perpendicular to the momentum of the nucleon. It is
measured in the DY process with transversely polarized beams. Specifically,
denoting the spin projection perpendicular to the momentum of the nucleon. It is
measured in the DY process with transversely polarized beams. Specifically,
where  is the polar angle of either lepton in the rest frame of the virtual
photon, and
is the polar angle of either lepton in the rest frame of the virtual
photon, and 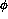 is the angle between the direction of polarization and the normal
to the plane of the dilepton decay.
is the angle between the direction of polarization and the normal
to the plane of the dilepton decay.
Unlike 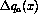 , very little is known about
, very little is known about 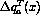 . Estimates
using the MIT bag model[14] indicate that
. Estimates
using the MIT bag model[14] indicate that 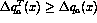 in the large-x
region where valence quark polarization predominates. No estimates are available for the antiquark
transversity,
in the large-x
region where valence quark polarization predominates. No estimates are available for the antiquark
transversity, 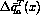 . We assume that optimization of the experimental conditions for
. We assume that optimization of the experimental conditions for
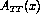 is similar to that presented previously for
is similar to that presented previously for 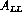 . The major differences are in the
angular dependencies of Eq. 7. For an axially symmetric detector the
. The major differences are in the
angular dependencies of Eq. 7. For an axially symmetric detector the 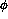 integration leads to a reduction of statistical
precision of
integration leads to a reduction of statistical
precision of 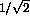 . Furthermore the
. Furthermore the  dependence of the muon system is not all
concentrated at
dependence of the muon system is not all
concentrated at 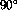 , as can been seen in Fig. 7, leading to a further
small reduction in statistical precision. Thus, given equal magnitudes of helicity and
transversity polarization effect, obtaining statistical significance for
, as can been seen in Fig. 7, leading to a further
small reduction in statistical precision. Thus, given equal magnitudes of helicity and
transversity polarization effect, obtaining statistical significance for 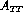 will be
more difficult.
will be
more difficult.
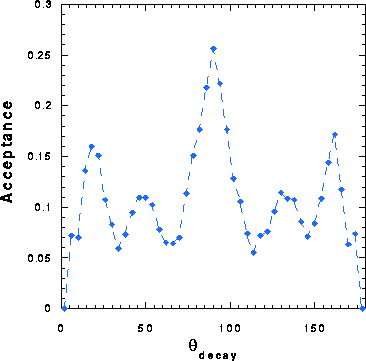
Figure 7: Decay angle acceptance of the upgraded muon spectrometer
for Drell-Yan pairs with 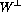 .
.