


Next: Global Alignment Requirements
Up: Muon Tracking
Previous: Muon Tracking
The internal alignment of the muon tracking stations in 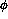 is
determined by the momentum resolution requirements of the tracker.
In order to obtain a mass resolution (which is dominated by
energy straggling in the material prior to the tracking stations)
on the order of 200
is
determined by the momentum resolution requirements of the tracker.
In order to obtain a mass resolution (which is dominated by
energy straggling in the material prior to the tracking stations)
on the order of 200 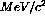 for the upsilon vector meson, a
spectrometer momentum resolution of less than 2% is required.
Simulations have shown that this can be obtained by three
tracking chambers at each measurement station
which have a
for the upsilon vector meson, a
spectrometer momentum resolution of less than 2% is required.
Simulations have shown that this can be obtained by three
tracking chambers at each measurement station
which have a 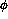 resolution of approximately 100
resolution of approximately 100 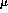 m (see
Figures 1 and 2). In
order to retain this momentum resolution, an alignment resolution
of much less than 100
m (see
Figures 1 and 2). In
order to retain this momentum resolution, an alignment resolution
of much less than 100 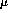 m is desired. We specify a
m is desired. We specify a 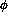 alignment criterion of 25
alignment criterion of 25 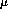 m inside the tracking volume.
m inside the tracking volume.
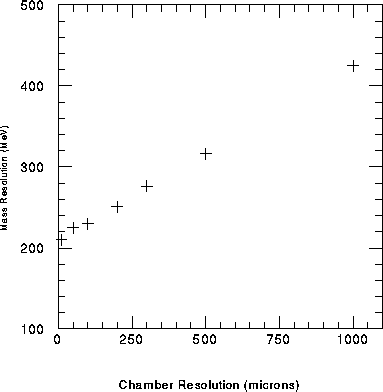
Figure 1: The upsilon mass resolution in the North arm versus
the chamber resolution.
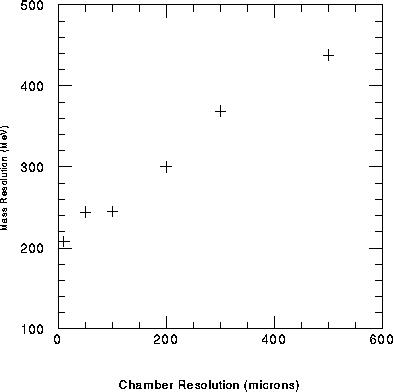
Figure 2: The upsilon mass resolution in the South arm versus
the chamber resolution.
Note: An x or y displacement of any station or individual
octant will translate directly into a phi error for most
octants. Therefore, it is necessary that x or y alignments
be known to 25 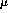 m, in addition to needing to know any phi
rotations to 25
m, in addition to needing to know any phi
rotations to 25 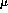 m.
m.
If muons which pass from octant 1 in station 1 to octant 2 in
station 2, for example, are to be tracked then the octant-to-octant
alignment requirements will be the same as the requirements specified
above, determined by the momentum resolution requirements. If
only tracks which pass through projective octants are to be
tracked, then the octant-to-octant alignment requirements
will be determined
by the opening angle resolution needed to achieve good mass
resolutions. The angular resolutions at the vertex are given
in the section on aligning the North and South muon arms, and are
on the order of 3-9 mRad. If this resolution, which is caused by
the multiple scattering in the absorber materials, is to be maintained,
then an octant-to-octant alignment on the order of 1.2 mm
in the x-y plane is
adequate (see North and South arm alignment section).
The muon tracking station-to-station alignment in z affects the
ability to measure the sagitta of a track (and thus the momentum)
in the tracker, the alignment of the stations with the magnetic field,
and the ability to measure the  angle of a track (and
thus the opening angle of dimuons from vector meson decay). To
determine exactly what the z alignment requirements are, a GEANT
study was done which took hits from upsilon dimuons and displaced
all station two hits by a fixed amount with respect to stations
one and three. The hits at stations one and three and the
displaced station two hits were then fit and the mass resolution
of the dimuons was calculated. Figure 3 shows
the resulting mass resolution vs. station two displacements.
As can be seen 0.5 and 1.0 mm displacements did not affect the
mass resolution, but a 1.5 mm displacement increased the mass
resolution by 15% to 250
angle of a track (and
thus the opening angle of dimuons from vector meson decay). To
determine exactly what the z alignment requirements are, a GEANT
study was done which took hits from upsilon dimuons and displaced
all station two hits by a fixed amount with respect to stations
one and three. The hits at stations one and three and the
displaced station two hits were then fit and the mass resolution
of the dimuons was calculated. Figure 3 shows
the resulting mass resolution vs. station two displacements.
As can be seen 0.5 and 1.0 mm displacements did not affect the
mass resolution, but a 1.5 mm displacement increased the mass
resolution by 15% to 250 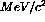 , and a 5 mm displacement
increases the mass resolution to 430
, and a 5 mm displacement
increases the mass resolution to 430 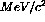 . We therefore
require a station to station alignment in z of at least 1.5/4 mm =
0.4 mm.
. We therefore
require a station to station alignment in z of at least 1.5/4 mm =
0.4 mm.
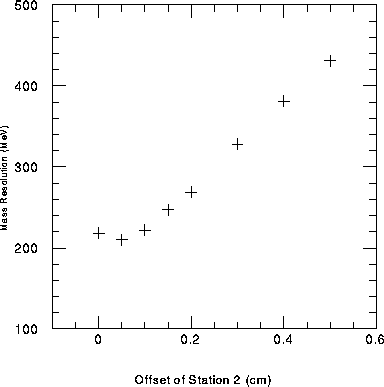
Figure 3: The upsilon mass resolution in the North muon
arm versus a displacement of the station two hits.



Next: Global Alignment Requirements
Up: Muon Tracking
Previous: Muon Tracking
Converted to HTML from LaTeX by W. Wayne Kinnison
Thu Aug 24 17:53:05 MDT 1995
 is
determined by the momentum resolution requirements of the tracker.
In order to obtain a mass resolution (which is dominated by
energy straggling in the material prior to the tracking stations)
on the order of 200
is
determined by the momentum resolution requirements of the tracker.
In order to obtain a mass resolution (which is dominated by
energy straggling in the material prior to the tracking stations)
on the order of 200 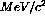 for the upsilon vector meson, a
spectrometer momentum resolution of less than 2% is required.
Simulations have shown that this can be obtained by three
tracking chambers at each measurement station
which have a
for the upsilon vector meson, a
spectrometer momentum resolution of less than 2% is required.
Simulations have shown that this can be obtained by three
tracking chambers at each measurement station
which have a 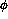 resolution of approximately 100
resolution of approximately 100 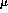 m (see
Figures 1 and 2). In
order to retain this momentum resolution, an alignment resolution
of much less than 100
m (see
Figures 1 and 2). In
order to retain this momentum resolution, an alignment resolution
of much less than 100 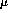 m is desired. We specify a
m is desired. We specify a 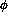 alignment criterion of 25
alignment criterion of 25 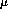 m inside the tracking volume.
m inside the tracking volume.


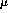 m, in addition to needing to know any phi
rotations to 25
m, in addition to needing to know any phi
rotations to 25 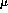 m.
m.
 angle of a track (and
thus the opening angle of dimuons from vector meson decay). To
determine exactly what the z alignment requirements are, a GEANT
study was done which took hits from upsilon dimuons and displaced
all station two hits by a fixed amount with respect to stations
one and three. The hits at stations one and three and the
displaced station two hits were then fit and the mass resolution
of the dimuons was calculated. Figure
angle of a track (and
thus the opening angle of dimuons from vector meson decay). To
determine exactly what the z alignment requirements are, a GEANT
study was done which took hits from upsilon dimuons and displaced
all station two hits by a fixed amount with respect to stations
one and three. The hits at stations one and three and the
displaced station two hits were then fit and the mass resolution
of the dimuons was calculated. Figure 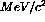 , and a 5 mm displacement
increases the mass resolution to 430
, and a 5 mm displacement
increases the mass resolution to 430 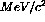 . We therefore
require a station to station alignment in z of at least 1.5/4 mm =
0.4 mm.
. We therefore
require a station to station alignment in z of at least 1.5/4 mm =
0.4 mm.
