Tian Wei - Mao Yajun - Wan Yude - Sun Zuxun - Zhou Shuhua
China Institute of Atomic Energy
(submitted: 24 January 1996)
The PHENIX project proposed to use the limited streamer tubes (LST) as muon's
detector. The collider's bunch time interval is about 112 ns, but the LST with
9 mm 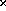 9 mm cross section has about 120 ns timing uncertainty. In order
to meet the timing requirement, one approach is to use the LST with smaller
cross section.
9 mm cross section has about 120 ns timing uncertainty. In order
to meet the timing requirement, one approach is to use the LST with smaller
cross section.
We constructed a 1 m long prototype LST. The tube is 5 mm 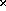 5 mm in
cross section, 24 units in each jacket. The extrusion was supplied by ORNL and
the rest was made at the China Institute of Atomic Energy. The tube was strung
with 50
5 mm in
cross section, 24 units in each jacket. The extrusion was supplied by ORNL and
the rest was made at the China Institute of Atomic Energy. The tube was strung
with 50 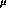 m diameter silver-plated copper beryllium wires at a tension of
125 g. We put a spacer in the middle of the tube to support the wires. The
wires were open circuit at one end and joined together through 200
m diameter silver-plated copper beryllium wires at a tension of
125 g. We put a spacer in the middle of the tube to support the wires. The
wires were open circuit at one end and joined together through 200  terminating resistors to a high-voltage connection at the other end. The
graphite painted extrusion electrode has a surface resistivity of
90 K
terminating resistors to a high-voltage connection at the other end. The
graphite painted extrusion electrode has a surface resistivity of
90 K /
/ . The graphite paint was made in a Shanghai graphite paint
factory. The paint was diluted with (CH
. The graphite paint was made in a Shanghai graphite paint
factory. The paint was diluted with (CH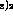 CHCH COCH
CHCH COCH and absolute
alcohol. We painted the extrusion three times.
and absolute
alcohol. We painted the extrusion three times.
A mixture of argon and isobutane Ar:C H
H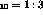 was used as a working gas
at one atmospheric pressure. Over a period of about† two weeks, the operating
voltage was gradually raised. When the high voltage can be raised to 3500 V
and the leakage current is less than 2
was used as a working gas
at one atmospheric pressure. Over a period of about† two weeks, the operating
voltage was gradually raised. When the high voltage can be raised to 3500 V
and the leakage current is less than 2 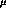 A, we consider the tube a good one.
A, we consider the tube a good one.
In July we performed a triple coincidence experiment to test the LST with cosmic ray. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the experiment arrangement and the electronics. This experiment was performed with a Micro VAX data acquisition system.
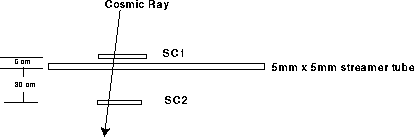
Figure 1: Sketch of the experiment arrangement.
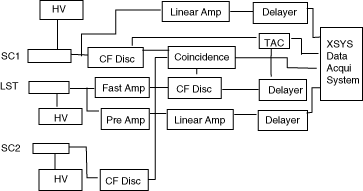
Figure 2: Electronics of the experiment.
We obtained the time and energy spectra (see Figures 3 and 4) at different high voltages for the LST working in a proportional mode. Results of the cosmic ray test are as follows:
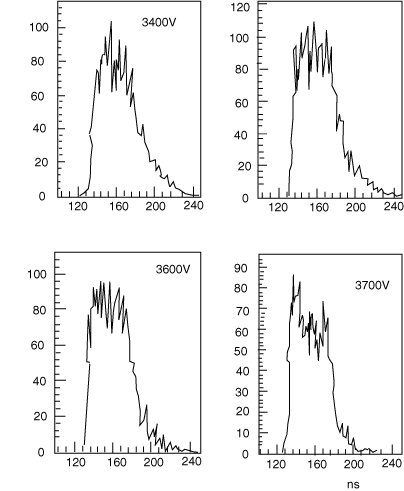
Figure 3: Time spectra at different HVs (Cosmic Ray)
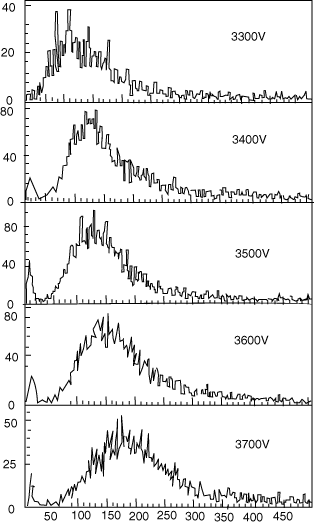
Figure 4: Energy spectra at different HVs (Cosmic Ray)