 m diameter gold-plated tungston wire
from LUMA. The other wire used is a 0.003" diameter copper-berylium wire from
R&F Alloy Wires, type C17200 pretempered wire.
m diameter gold-plated tungston wire
from LUMA. The other wire used is a 0.003" diameter copper-berylium wire from
R&F Alloy Wires, type C17200 pretempered wire.
Stress strain calculations and tests were conducted on the two types of wires
to be used in the construction of the Cathode Strip Chambers which will be the
muon tracking detectors for PHENIX. One of the types of wires is a 20  m diameter gold-plated tungston wire
from LUMA. The other wire used is a 0.003" diameter copper-berylium wire from
R&F Alloy Wires, type C17200 pretempered wire.
m diameter gold-plated tungston wire
from LUMA. The other wire used is a 0.003" diameter copper-berylium wire from
R&F Alloy Wires, type C17200 pretempered wire.
The gold coating on the tungsten wire is 4% by weight of the wire, and is applied over a flash coating of nickel that is first plated directly onto the tungston core. That technique of manufacturing the wire gives the gold a much stronger bond to the wire, and helps to avoid the problem of "pealing". The gold coating will then withstand soldering temperatures up to 870deg. C. It is advisable that a soldering temperature of 700 - 750deg. F be used with tin-lead solder. When soldering this wire it is also important to avoid direct contact of the solder tip with the wire, and keep the soldering time as short as possible.
Samples of both of the wires were tested at the Material Science and Technology Division at Los Alamos, the results of those tests are shown in the Figures 1 and 2. The copper wire was very consistent over several tests. It yields at about 1 GPa. The ultimate strength is about 1.2 - 1.3 GPA (600 grams) at about 2.5% total strain which is typical and consistent with the literature supplied by the company. It is suggested that in order to maintain loading within the elastic region a load of no more then 350 grams be used.
In the case of the tungston wires several tests were made. There was a problem of wire slipage in the clamps which invalidated the strain measurement. Loads up to 2 GPa in stress, which is about 70 grams, were applied. That is a safe working load limit (70 grams) to avoid brittle fracture which is predicted to occur at about 1% strain and 4 GPa stress (about 140 grams).
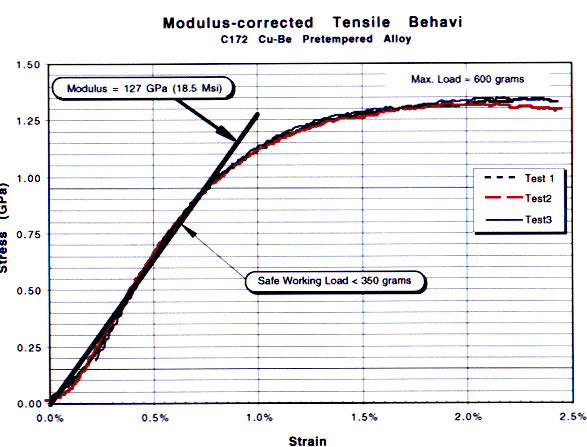
Figure 1: Stress-Strain results for 3.0-mil copper-berylium wire.
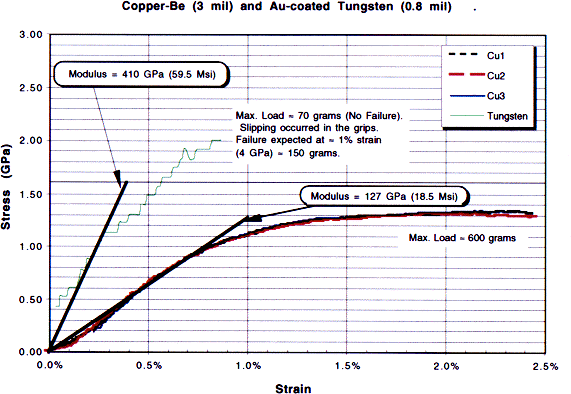
Figure 2: Stress-strain results for 0.8-mil gold-plated tungsten and 3-mil copper-berylium wire.