
Send mail to Y. Nakada
Report of Muon ID chamber R&D at Kyoto
Y. Nakada
Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
and
Y. Mao
China Institute of Atomic Energy (CIAE), Beijing, P. R. China
and
RIKEN, Institute for Physical and Chemical Research, Hirosawa, Wako, Japan
(phenix-muon-96-11;
submitted: August 13, 1996)
Recent progress is reported for the Iarocci tube R&D in Kyoto University.
The contents are the write up version of the presentation in Santa Fe.
We have tested the Iarocci tubes for Muon ID whose characteristics are;
- 9mm by 9mm cell
- 100 micro meter gold plated tungsten wire anode
- Carbon varnish PVC cathode
- 8 cells per tube
- 1 readout per tube
- length about 5m
- characteristic impedance of one cell is ~220 ohm
In Kyoto we have 10 tubes made in Italy, and 4 tubes assembled in China.
Of the Chinese tubes all components are made in Italy or USA, and hand assembled in China. Besides these tubes, 20 more tubes genuinely made in China are on a ship to Kyoto.
Italian tubes have low resistive cathode and Chinese ones are high resistive.
|
length |
cathode resistance |
| China tube |
5.0m |
700k ohm |
Italy tube |
5.1m |
2k ohm |
|
Followings are our major concerns on the R&D studies
- Comparison Italian and Chinese tubes (properties, reliability etc.)
Tested two kind of tubes
- A tube, all components made in Italy or USA, assembled in China
- A tube made in Italy
- Determination of gas mixture
Tested two kind of gas mixture
- Argon:isobutane 1:3 (Normal gas)
- CF4:isobutane 1:1 (Fast gas)
- Choice of operation mode
Tested at Limited Streamer mode and proportional mode.
We have checked following characteristics, which are very important to
define a good tube, for one Italian tube and one Chinese tube.
- plateau (start HV, plateau stretch and slope)
- pulse height (gas gain, related to design pre amplifier)
- time spread
- pulse shape (express difference)
- efficiency
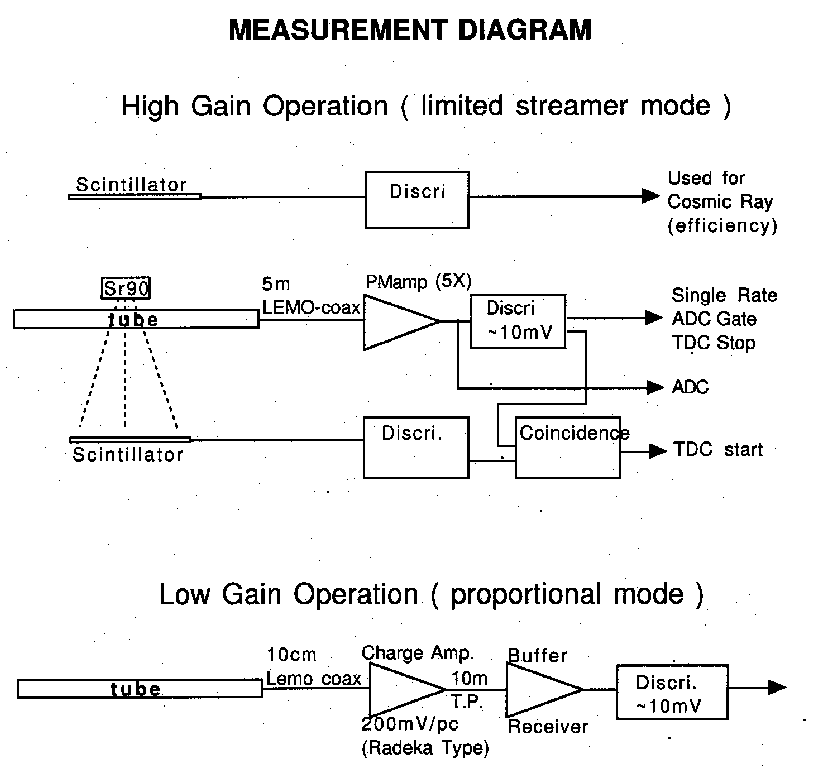
The test setup schematic is shown below.
In the limited streamer mode operation, a tube is connected to 5m coaxial cable followed by a x5 PM amplifier and a typical NIM discriminator with a threshold of ~10mV.
In the proportional mode test, a tube is directly connected to charge sensitive preamplifier (200mV/pC) which drives 10m twisted pair cable followed by a buffer receiver and a discriminator (~10mV threshold).
Test setup
Limited streamer mode test
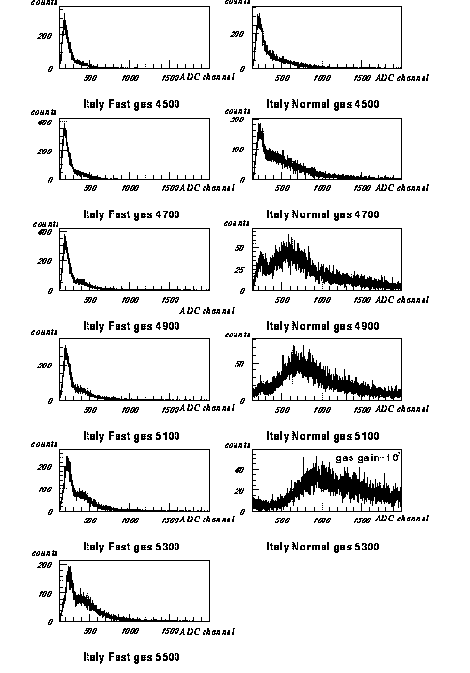
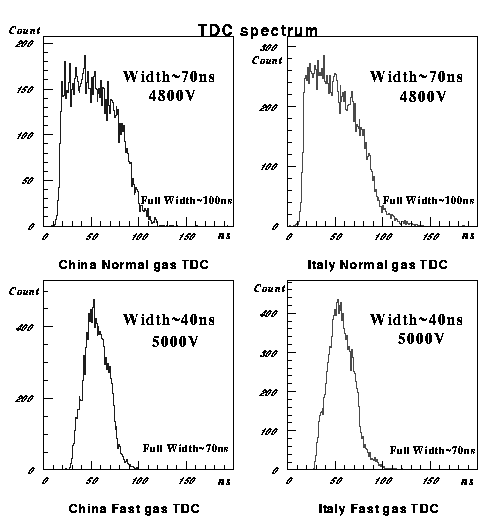
Here shown are the pulse height spectrum at different high voltages for the two types of gas mixture.
Peaks around 250ch are proportional mode peaks, and peaks around 1000ch are streamer mode peaks.
With Normal gas, limited streamer mode starts from 4700V and entering into streamer mode completely at 5200V.
With Fast gas, limited streamer mode starts from 4900V and discharge starts before the end of limited streamer mode.
Gas gain is about 107 at 1000ch of ADC.
This graph is taken with an Italian tube and a Chinese tube has shown very similar behavior.
We examined position dependence of the pulse hight over the effective area.
The variety is less than something like 20%, mainly due to the signal attenuation over the tube-length.
ADC spectrum at different voltages(Italian tube)
Signal arrival time distributions are shown here. Apparently the time spread is shorter with Fast gas. Please note that the shape is different for the gas mixtures. The rise of spectrum is very soft with Fast gas. The reason is not understood yet.
Time spectra with Fast gas and Normal gas, in limited streamer mode
This table below shows efficiencies taken with Fast gas at 5000V. We observed the efficiency is about 90% with both tubes.
|
efficiency |
statistical error |
| China tube |
90.0% |
+-1.4% |
Italy tube |
89.2% |
+-2.5% |
|
Proportional mode test
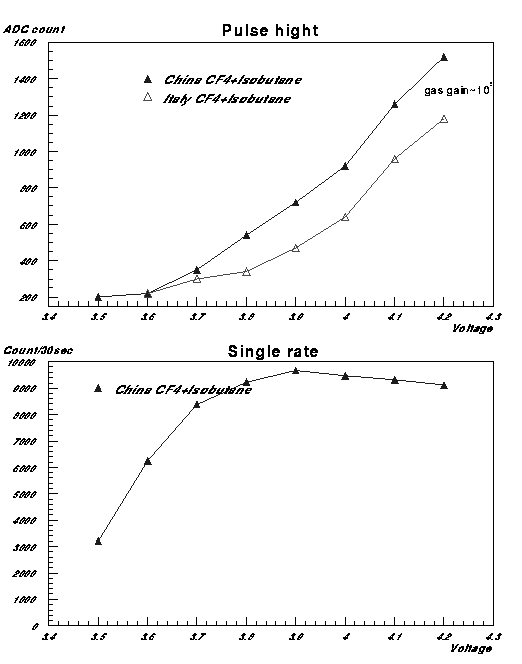
Proportional mode operation is done with Fast gas. Average height and Signal rates are shown as function of applied High voltage. Gas gain is about 105 at 1000ch. At 3900V reached single rate plateau.
Pulse height as a function of high voltage (top) and Single count rate (bottom)
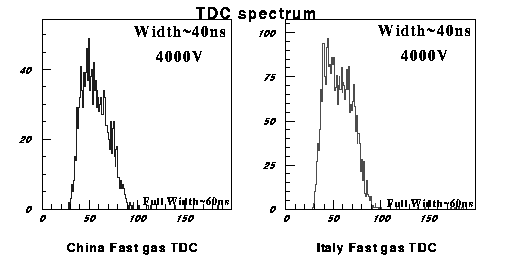
We have also examined the time response.
The shape of the spectra is different from limited streamer mode.
The tail is shorter, and rising is faster. The difference may be due to the relatively lower threshold compare to signal in proportional mode than in limited streamer mode.
Time spectra with Fast gas in proportional mode
This table is efficiency taken with Fast gas, at 4000V. The efficiency is higher than in limited streamer mode, and this effect also come from lower threshold compare to signal.
|
efficiency |
statistical error |
| China tube |
93.7% |
+-2.2% |
| Italy tube |
93.6% |
+-1.4% |
Gas leak problem
At the beginning of the test we were suffered from heavy gas leakage from tubes.
The source of the leak are summarized as
- Connection between endcap and box
- 4/10 Italian tubes and 1/4 Chinese tubes have loose connection.
- Endcap fabrication
- 1/10 Italian tubes has two pinholes in the endcap.
- gas connector
- Some connectors are loose and some packing rubbers are rotten.
Most of them are fixed with silicon grease (RTV) and Teflon tape.
We, however, definitely need a better Quality Control.
Pressure drop question
Another issue is pressure drop question.
Namely, how many tubes can be connected in series?
So we connect 4 tubes series, then flow the gas at a rate of 500cc/min.
At the inlet pressure is 5.1mbar, at outlet 2.8mbar (0.6mbar/tube).
Main pressure drop is caused in the connecting synflex tube.
Additionally we observed a tube broken at 60mbar over pressure.
So, a kind of strategy for the gas flow operation is as follows.
At assembly time, each tube should be tested at 30mbar over pressure and operated below 10mbar at any time. For the starting time we flow 100cc/min (3%/min of the volume of 3l) and running time 10cc/min.
This leads that maximum 40~50 tubes can be connected in series to ensure the pressure criteria. With this assumption gas flow condition is summarized as follows.
|
Starting time (100cc/min) |
Running time (10cc/min) |
| 1 tube |
pressure drop |
0.1mbar |
0.01mbar |
| time of one volume exchange |
32.4min |
324min |
| 50 tubes series |
pressure drop |
5mbar |
0.5mbar |
| time of one volume exchange |
27hour |
270hour |
| 18000tubes(50seriesx408panel) gas usage per day |
58.75m3 |
5.875m3 |
|
|
|
Casing and termination
Typical pulse shape of streamer signal is as shown below.
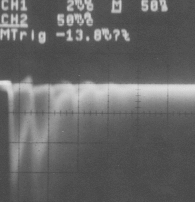 Chinese Tube (no termination)
Chinese Tube (no termination)
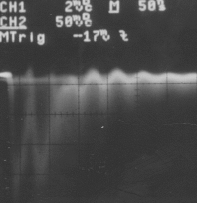 Italian Tube (no termination)
Italian Tube (no termination)
Chinese and Italian tubes show no significant difference in spite of the cathode resistivity. (700k ohm vs 2k ohm)
Signal reflection at the end of tube is observed.
The reflection can be terminated at the non-readout end. This picture below shows terminated signal, but still have some after effect.
Since cathode resistance is so large, termination must be done to the shield cover.
In any operation mode proper shielding is indispensable to reduce noise level
reasonably.
For the moment we are using just aluminum foil.
Summary
Our major bottom lines are;
- Chinese assembly is as reliable as Italian.
- Fast gas is equally stable as Normal gas.
- Both proportional mode and streamer mode have enough efficiency.
- Same time resolution in limited streamer mode and in proportional mode.
- Fabrication requires better quality control.
Notes
In streamer mode operation, sometime spontaneous discharge starts, stays several minutes, and stops. We will try to solve this problem, but preferring lower gain operation for the stability.
We will continue similar study for the genuine Chinese tubes. The results will determine the place of the fabrications.
Long time stability (endurance test with high current) will be studied in this summer.
Last Update: 13 September 1996
Page maintained by Muon Arms Webmaster, Mail Stop H846, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM 87545.

 Chinese Tube (no termination)
Chinese Tube (no termination)  Italian Tube (no termination)
Italian Tube (no termination)